Improving SCADA Communications with Cellular Networking
Cellular routers play a critical role in SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) communication systems by providing reliable and secure wireless connectivity to remote assets, such as sensors, meters, and other devices.
In SCADA systems, data is collected from remote devices and sent to a central location for analysis and control. In many cases, these remote assets are located in areas that are difficult to reach or in harsh environments where wired connectivity is not feasible. This is where cellular routers come into play.
Cellular routers provide wireless connectivity using cellular networks, such as 4G or 5G. They act as a bridge between the remote devices and the central SCADA system, allowing data to be transmitted securely and in real-time.
Cellular routers can also be used to establish a VPN (Virtual Private Network) connection between the remote devices and the central SCADA system. This ensures that the data transmitted between the devices and the central system is encrypted and protected from unauthorized access.
Moreover, cellular routers can be equipped with advanced features such as failover capabilities, which ensures that the SCADA system stays connected to the remote devices even if the primary cellular network is down. This helps to minimize downtime and ensure that critical data is always available.
Overall, cellular routers are an essential component of modern SCADA communication systems as they provide reliable and secure wireless connectivity to remote assets, helping to ensure efficient and effective monitoring and control of critical infrastructure.
However, like any technology, it also has its limitations. In this article, we will explore the benefits and challenges of cellular communications for utilities within SCADA-based applications. We'll also explore ways to overcome those challenges to ensure the highest efficiency levels possible.
Advantages of Cellular Communications
Wide Coverage Area
Cost-Effective
Cellular communication is often more cost-effective than other communication options such as satellite or microwave, especially for small to medium-sized utility companies. Cellular communication can be more cost-effective in many cases than building and maintaining a dedicated communication infrastructure.
High Bandwidth
Cellular networks offer high bandwidth, essential for real-time data transmission and remote control of utility operations. This can be especially beneficial in utility SCADA systems where real-time data is critical for making informed decisions.
Scalability
Cellular networks are highly scalable, allowing utility companies to add or remove devices and users as needed without additional infrastructure. This can be especially useful for utility SCADA systems that require frequent updates and modifications.
Security
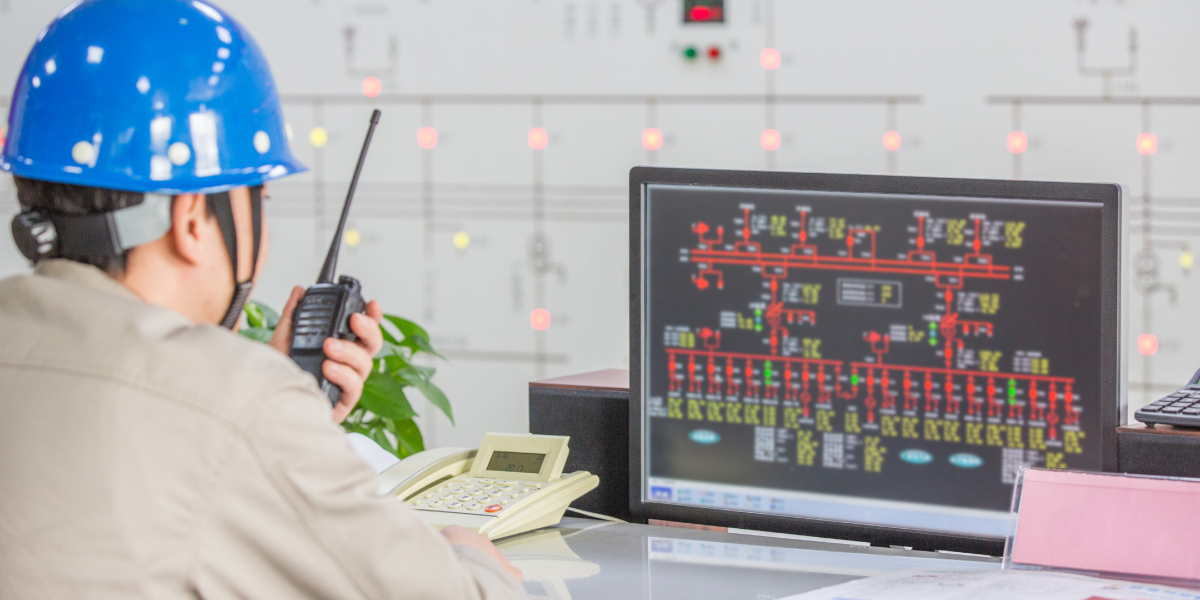

Potential Limitations of Cellular Communications
Signal Strength
Bandwidth Limitations
Latency
Regulatory Restrictions
Network Congestion
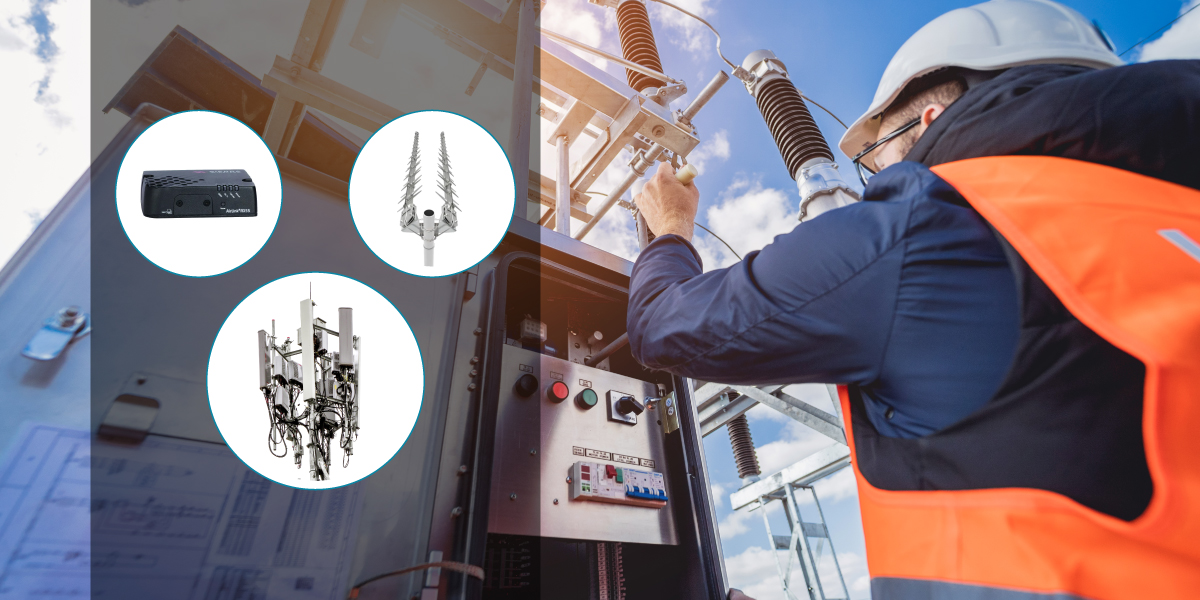

Ways to Overcome The Limitations
Improve Signal Strength
To overcome this limitation, utility companies can use high-gain antennas that operate over long distances to improve signal strength in areas with weak signals. Additionally, choosing one or more cellular providers with the best coverage in the area can also help improve signal strength. Antennas like Poynting’s LPDA are particularly great at boosting LTE signal strength over long distances.
Manage Bandwidth Limitations
Reduce Latency
To reduce latency, utility companies can use low-latency cellular networks* or prioritize data transmissions to reduce delays. They can also use edge computing technologies to process data closer to the SCADA devices, reducing the amount of data that needs to be transmitted over the cellular network. Less congested LoRaWAN-based communications are also a viable option that USAT can provide guidance on as well for low-power low-data applications.
Ensure Regulatory Compliance
To ensure regulatory compliance, utility companies should work with cellular providers that comply with local regulations and obtain any necessary licenses and permits. They should also consider using alternative communication options as backup communication options in case of regulatory restrictions, like those mentioned in the previous recommendation; gated networks, private LTE, or microwave backhaul.
Address Network Congestion

*Low Latency with 5G
In Summary
Cellular communication offers many advantages for utility SCADA systems, including wide coverage area, high bandwidth, cost-effectiveness, scalability, and security. However, it also has its limitations (all of which can be overcome), including signal strength, latency, bandwidth limitations, network congestion, and regulatory restrictions. Utility companies should carefully consider these factors when deciding whether to use cellular communication for their SCADA systems and should explore additional redundant communication options as well to ensure reliable and secure operations.
About USAT
Our team not only helps you select, provision, and activate devices, we make sure they work in practical applications and real-life situations.
For over 25 years, USAT has provided cellular networking solutions for public and private utilities across the USA. With our extensive catalog of world-class routers, gateways, and software designed for remote monitoring and management in even the harshest environments — you can count on us to get and keep you connected.
Reliable connectivity translates to less manual equipment maintenance, reduced downtime, and an overall increase in your business's ROI. Contact the experts at USAT to learn how our wireless networking solutions can help meet your organization's exacting needs.
Share this Post